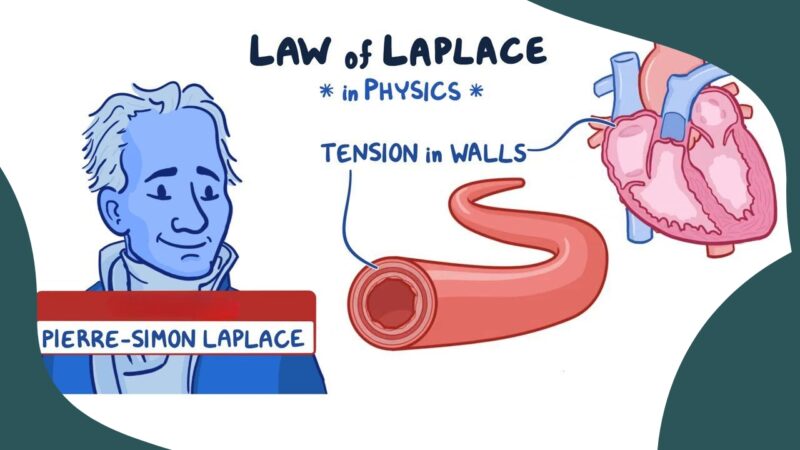
In our vast universe filled with profound mysteries and mathematical wonders, the Law of Laplace stands out as a testament to human ingenuity. This fascinating concept, discovered by the illustrious French mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace, intricately ties together the realms of physics and physiology.
In this piece, we will embark on a captivating journey through the world of the Law of Laplace, decoding its complexities and marveling at its applications.
Definition: The Brilliance of Pierre-Simon Laplace
The Law of Laplace is not just a mere mathematical formula, but a window into understanding the intricacies of pressure-volume relationships in spheres. Given the prominence of spherical structures in nature, from celestial bodies to the human body, it’s unsurprising that the Law of Laplace has far-reaching implications.
Where:
- Pressure represents the force exerted per unit area inside the sphere.
- Thickness is the measurement of the sphere’s wall.
- Tension captures the stress or force within the sphere’s wall, and
- Radius is the distance from the center of the sphere to its outer edge.
Conceptual Deep Dive
At its heart, the Law of Laplace conveys a fundamental truth: the tension experienced by a sphere’s wall is intrinsically linked to its thickness.
Understanding the Relationship
Imagine a balloon. If the balloon is inflated to its maximum capacity, the tension on its thin walls is palpable; one tiny prick and it bursts! Now, consider replacing that balloon with a rubber ball of the same size but with thicker walls.
The rubber ball can withstand more external force than the balloon, even if they are both filled to the same pressure. This difference in resilience, even at the same pressure level, is a manifestation of the Law of Laplace.
Breaking it Down
- Tension and Thickness: At a constant pressure, if we increase the thickness of the sphere’s wall, the tension decreases. This means that a sphere with a thicker wall will experience less stress or strain than one with a thinner wall, even if they are filled to the same pressure. This principle is why a heart with thicker walls can pump blood with less strain than one with thinner walls.
- Tension and Radius: When the radius of the sphere increases while keeping the thickness constant, the tension within the wall will increase. This concept can be visualized by considering a small balloon and a large one. The larger balloon, when inflated, will have its walls stretched more, thus experiencing more tension.
Relevance in Physiology
The Law of Laplace isn’t just a mathematical curiosity; it holds deep physiological importance.
The Human Heart
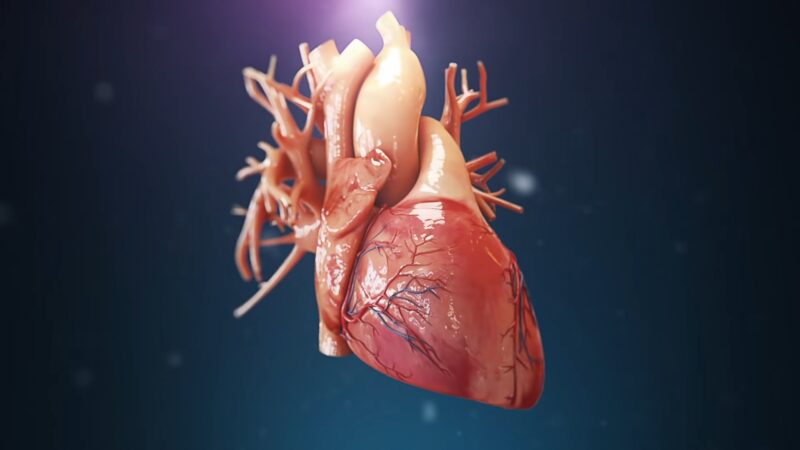
The heart’s chambers are akin to spheres, pumping blood throughout the body. According to the Law of Laplace, the tension in the heart walls can be reduced by increasing the thickness of the myocardium (the muscle tissue of the heart). This principle partly explains why athletes, whose hearts pump more blood, often have thicker heart walls.
The Alveoli
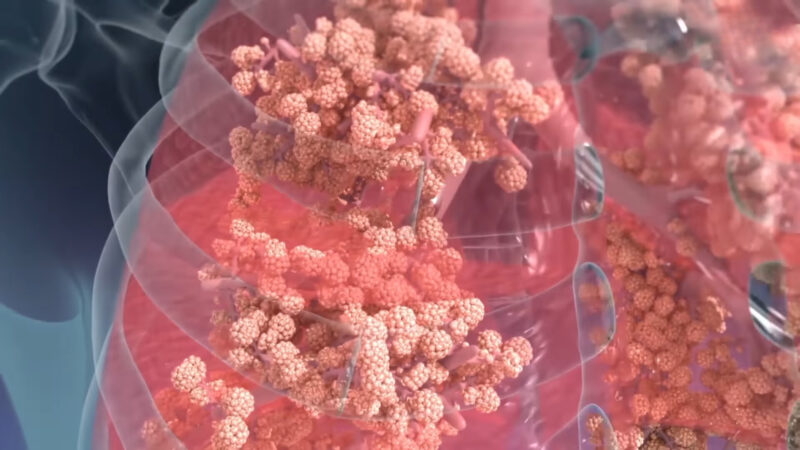
The tiny sacs in our lungs, known as alveoli, are responsible for the vital exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Their function can be better comprehended through the lens of the Law of Laplace.
Alveoli operate best when they maintain a balance – not too inflated and not too deflated – ensuring optimal gas exchange. The relationship between the tension in the alveolar walls and their radius ensures they don’t collapse and can efficiently perform their respiratory function.
In Conclusion
The Law of Laplace is a testament to the interconnectedness of our universe, where a mathematical principle can seamlessly translate into a deeper understanding of our very physiology. Pierre-Simon Laplace’s discovery bridges the gap between the abstract world of numbers and the tangible reality of our biological systems.
The next time you feel your heartbeat or take a deep breath, remember the brilliance of Laplace’s insights. Such laws don’t just exist in textbooks; they operate within us, dictating the rhythms of our existence. The magic of mathematics is not just in solving equations but in understanding the universe, and ourselves, a little bit better.